Galleries
Browse our highlight galleries with selections of Fermilab’s best photos, videos and graphics, and check out the Fermilab YouTube channel. Please contact creativeservices@fnal.gov to ask for permission for use.
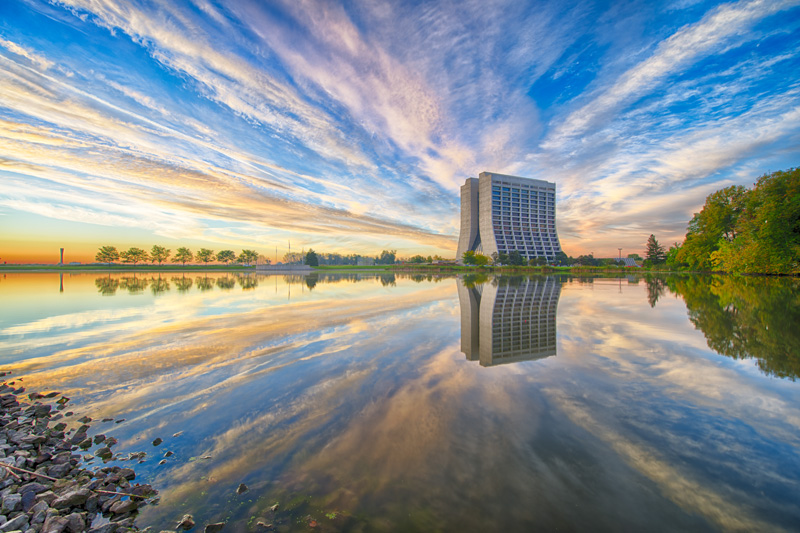
Best of Fermilab
The 'Best of' gallery shows media assets that best represent the activities that go on at Fermilab.
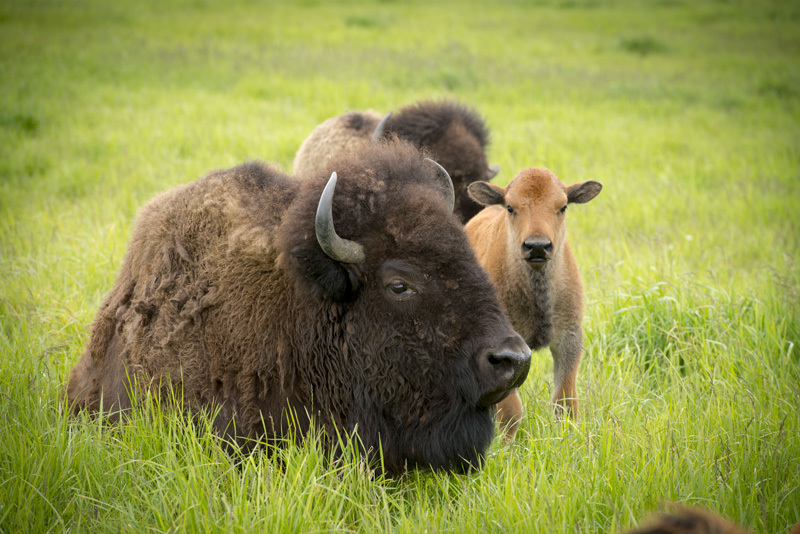
Bison
Fermilab's first director brought bison to the lab in 1969 as a symbol of the history of the Midwestern prairie and the laboratory’s research at the frontiers of particle physics.
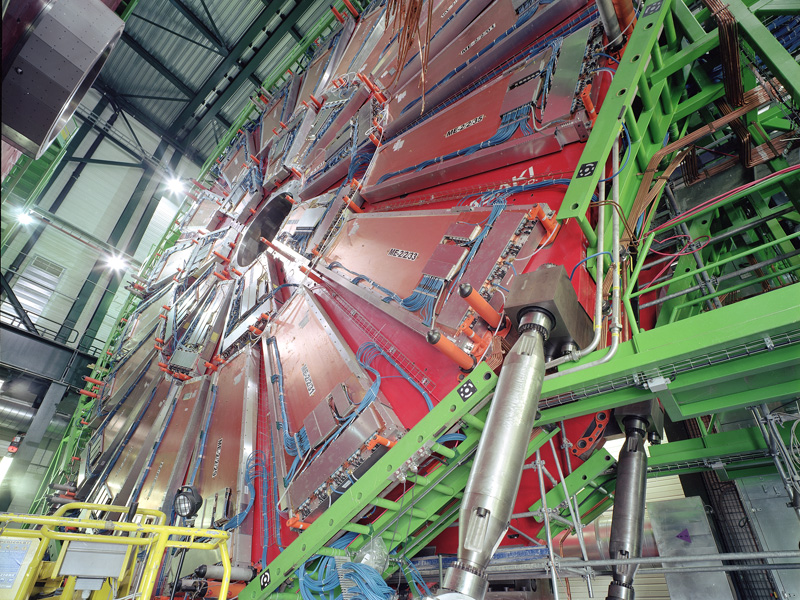
CMS experiment at CERN
Fermilab is the hub for more than 1000 U.S. physicists participating in the CMS experiment at CERN and plays a leading role in detector construction and operations, computing and software, and data analysis. Additional imagery is available from CERN.
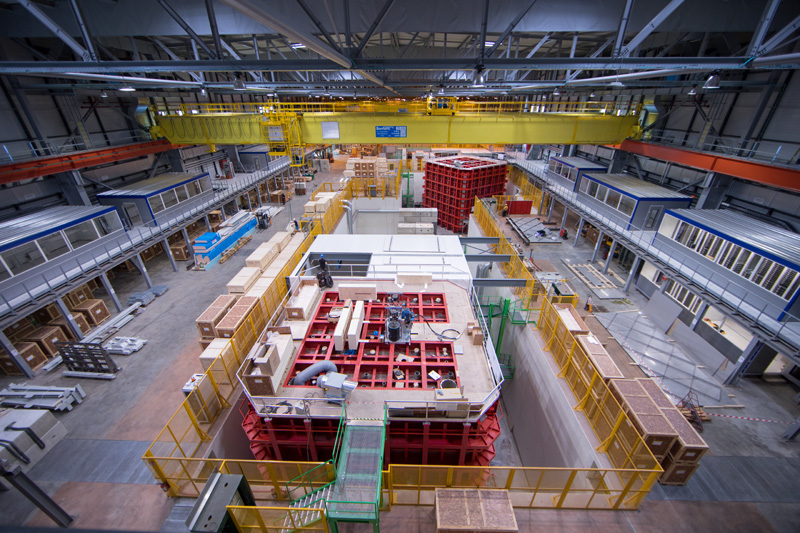
DUNE at LBNF
The Deep Underground Neutrino Experiment is an international flagship experiment to unlock the mysteries of neutrinos. It’s powered by the infrastructure of the Long-Baseline Neutrino Facility. Additional imagery is available from some of DUNE’s international partners, including CERN and Sanford Lab.
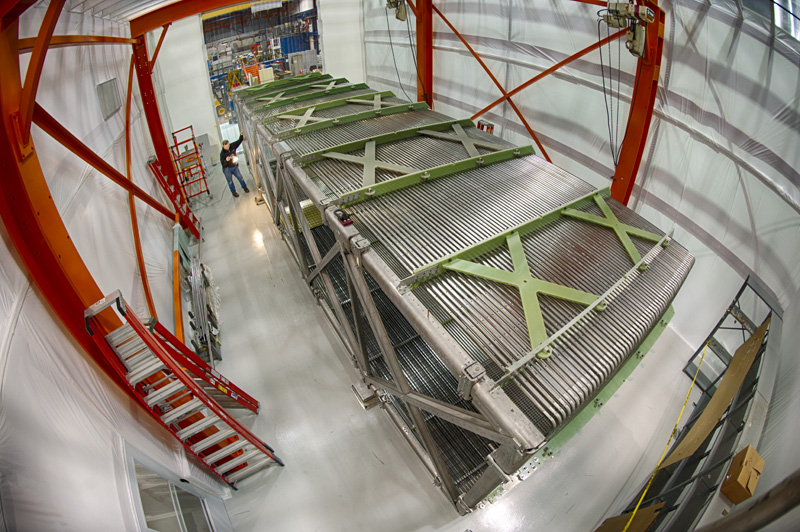
ICARUS
The ICARUS neutrino detector is searching for sterile neutrinos as part of Fermilab’s Short-Baseline Neutrino program. The detector began life at Gran Sasso Laboratory in Italy and was refurbished at CERN before joining the neutrino hunt at Fermilab.
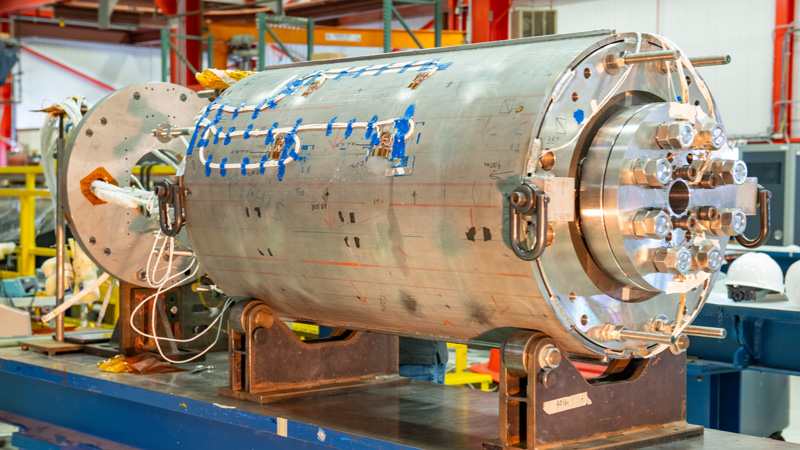
Magnets at Fermilab
Fermilab is a world leader in the design, fabrication, testing, and use of magnets. These powerful pieces of technology are essential equipment in particle accelerators and particle physics experiments.
MicroBooNE
The MicroBooNE experiment at Fermilab uses a school bus-sized detector to study fundamental particles called neutrinos.
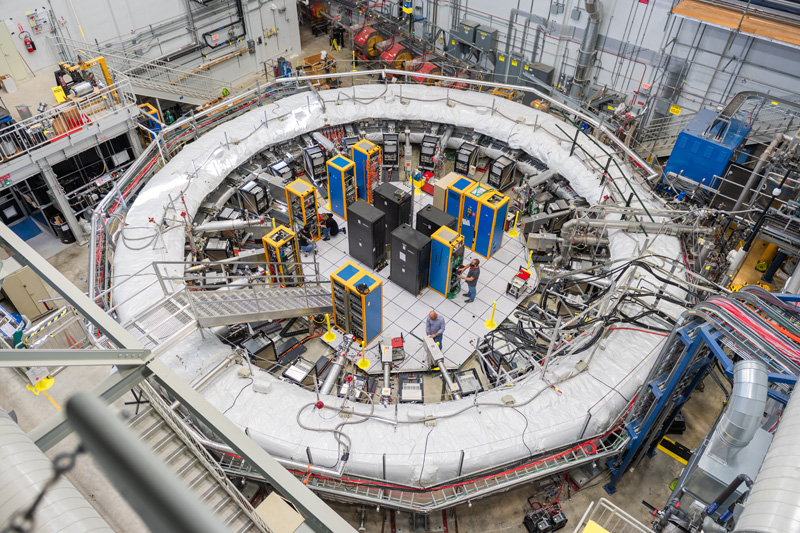
Muon g-2
The Muon g-2 experiment uses a 50-foot-diameter magnet and Fermilab’s powerful accelerator complex to explore how muons interact with a magnetic field. It’s a test of the Standard Model, where a discrepancy between theory and experiment hints at new particles or forces at work.
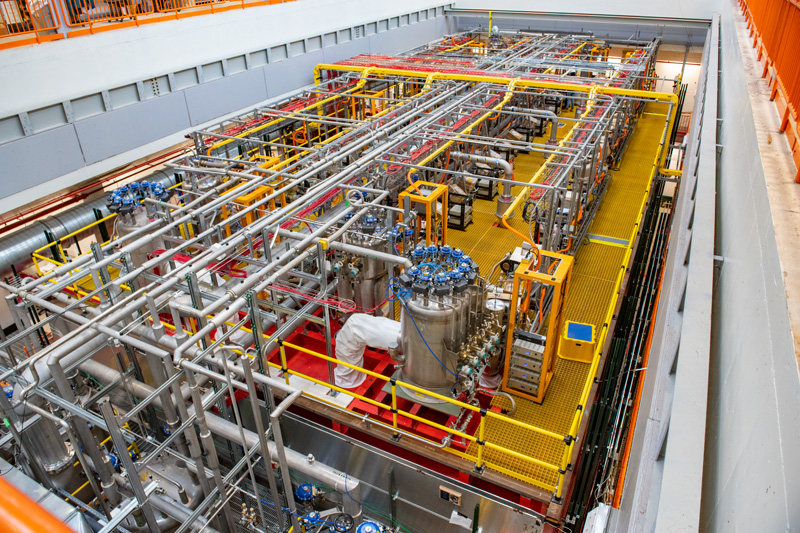
PIP-II
PIP-II is the upgrade project to improve Fermilab’s already impressive accelerator complex and create the intense particle beam required for DUNE. One feature of the upgrade is a brand new linear accelerator, the device at the start of Fermilab’s accelerator chain.
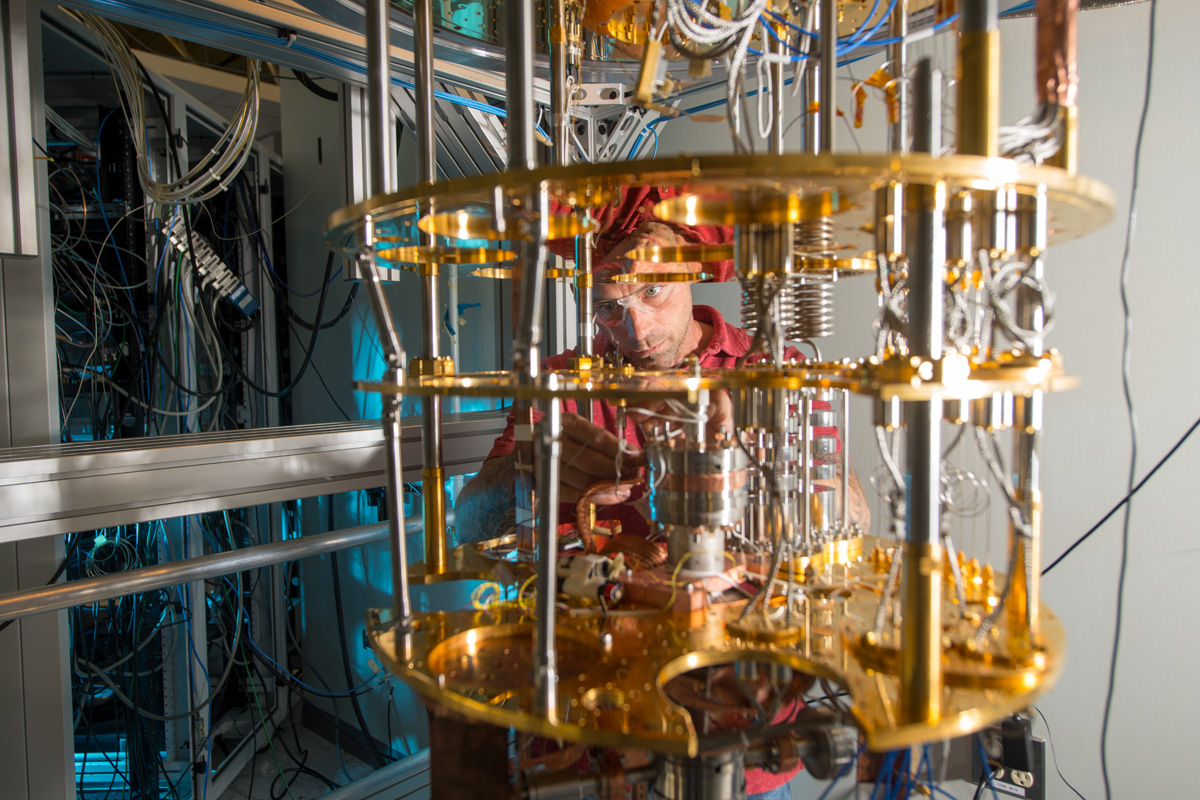
Quantum science and technology
Fermilab and partners are working together to solve the challenges of quantum sciences and technology. This includes building a state-of-the-art quantum computer and research on coherence time (how long qubits can maintain their quantum state), entanglement (the phenomenon in which the quantum states of two or more qubits are correlated), and algorithms (the set of tasks for a quantum computer to solve a problem).
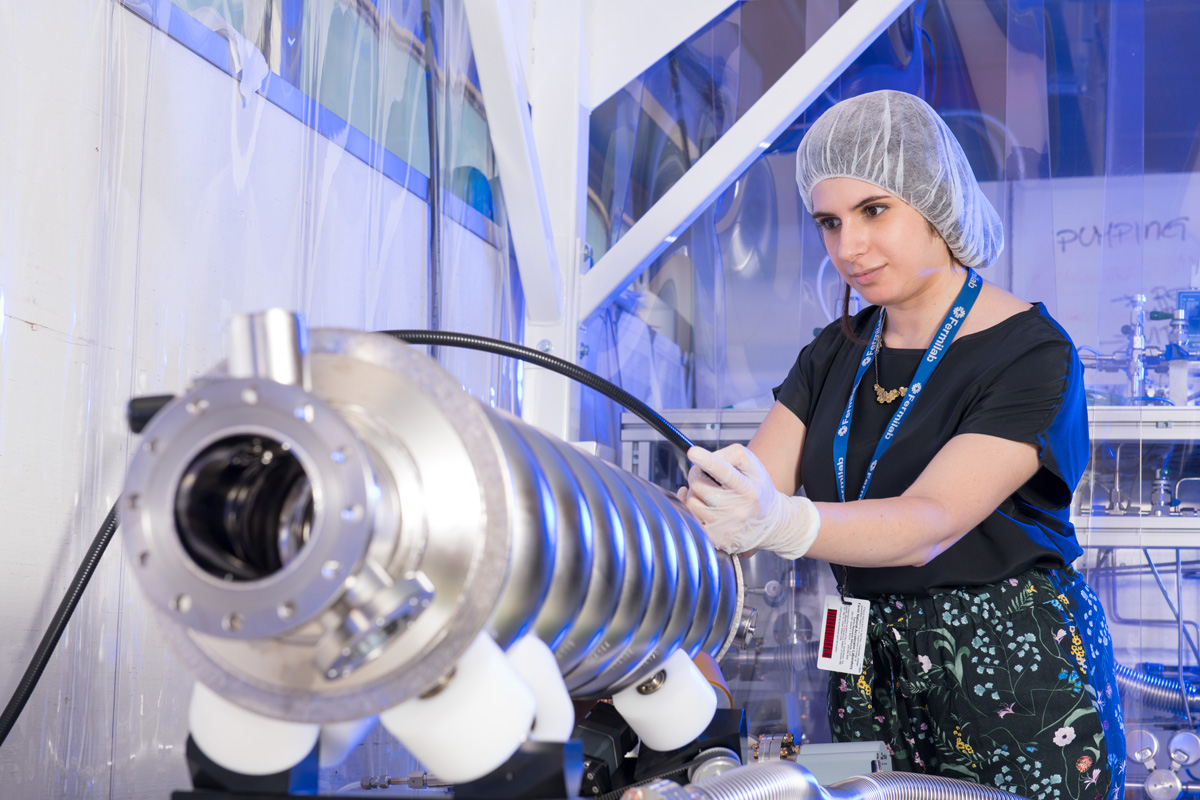
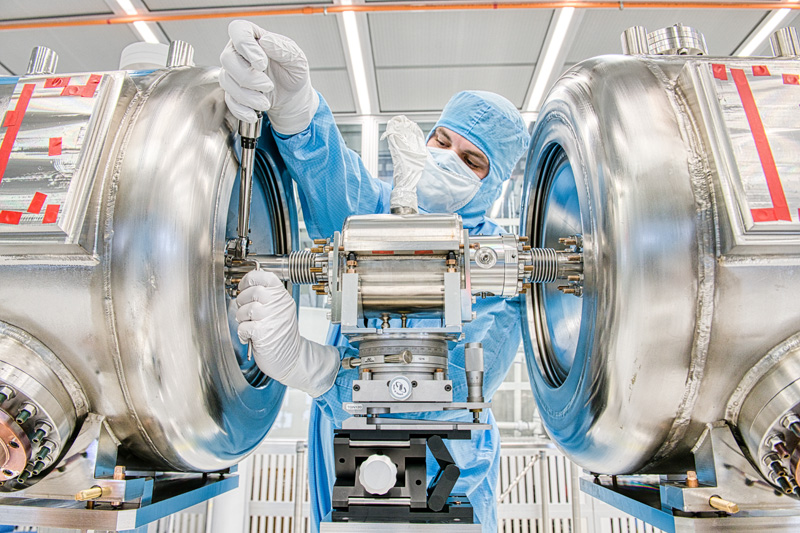
Superconducting radio-frequency technology
Superconducting radio-frequency (SRF) technology is one of the key elements for advanced particle accelerators and certain physics experiments. Superconducting materials are cooled to incredibly low temperatures and conduct current with little or no electrical resistance.
-
Fermilab creative assets library is managed by Fermi Forward Discovery Group, LLC as manager and operator of the Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory for the U.S. Dept. of Energy’s Office of Science. Copyright 2024 Fermi Forward Discovery Group, LLC. All Rights Reserved.
To request permission to use Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory visuals, footage, or media materials, please email Creative Services or call +1 630-840-3349. Requests should specify the way in which the images or footage will be used and permissions are granted only for those specified purposes. Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory materials that are downloaded or obtained through request may not be altered.
Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory visuals, footage, or media materials may not be used for commercial or advertising/marketing purposes or in any way that implies an endorsement of any company, product, or service by the Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory, or the manager and operator of the Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory, or the United States Department of Energy. Please apply Fermilab’s standard credit format when using visuals, footage or media materials. This includes “Credit: [Author’s name], Fermilab (or provided institution)”.